KERV is a proud contributor to the IAB – Interactive Advertising Bureau Data-Driven Video Best Practices guide alongside companies such as ABC, Adobe, CBS, Google, Hulu, NBC, SpotX, Sony, Verizon and more. The marketer’s guide is a valuable industry resource for professionals to learn about the state of data-driven video along with benefits, best practices, tips, etc.
Check out this important industry document, and see KERV’s three featured campaign examples for Carhartt, eBay and Fisher & Paykel. The following information was taken from IAB.com. Click the button below to see the full PDF.
Project Overview
As data fuels the digital advertising ecosystem and video consumption continue to rise, data-driven video is emerging as a powerful marketing tactic and strategy that enables brands to deliver innovative storytelling. The goal of this best practices document is to illustrate how marketers can utilize data to inform not only targeting efforts but the actual video assets and creative messaging. This document highlights the state of data-driven video, marketer benefits, tips for how to get started, best practices, and more.
IAB compiled data-driven video case studies to bring to life how data can be used to inform the video creative itself. These case studies showcase a variety of tactics and span across multiple brand verticals. Click here to view the video assets and learn about the campaign goals, data sets that were utilized, and results.
Data-Driven Video Overview
Data-driven video (DDV) is both a strategy and a tactic that allows marketers to use available data to deliver tailored advertising through precise audience targeting and personalized video creative that allows for permutations based on signals about the audience or other external factors. Underlying this strategy are two fundamental questions: who do you want to show this ad to and what messaging will move this individual to take a step towards the next best action?

(Source: Flashtalking)
Growth of Data-Driven Video
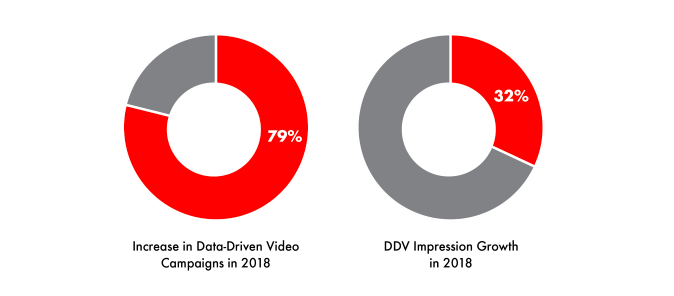
Benefits
- Consumers like personalization: According to an Epsilon study, 80% of respondents indicated they are more likely to do business with a company if it offers personalized experiences and 90% indicated that they find personalization appealing (Source: Epsilon, The power of me: The impact of personalization on marketing performance, 2018)
- Personalized video can result in more efficient media planning: By serving more relevant ads, marketers will be able to serve fewer, more impactful impressions.
- Data-driven video drives engagement: According to Innovid, there was a 78% lift in engagement rate on DDV campaigns compared to traditional pre-roll video ads (Source: Innovid, 2018 Global Video Benchmarks).
- Marketers pursue DDV to drive sales and lifetime value: According to a Verndale survey, personalization is most important for increasing sales and improving customer satisfaction and retention (Source: Verndale, Jan 2018). In addition, a SundaySky study revealed that personalized video experiences can improve Net Promoter Scores, which measure customer loyalty to a brand, by 48 points or more (Source: SundaySky, A Study of Personalized Videos Deployed by F500 Brands, February 2019).
Data Signals Used to Inform Targeting and Creative
- Contextual: page-level content via semantic analysis (i.e. headlines, article content) or video-level content
- Demographics (age/sex)
- Device level data (device make/model, browser, operating system)
- First-party (CRM, product feeds, etc.)
- Location data
- Prior ad exposure (enables sequential messaging)
- Psychographics
- Purchase history
- Real time data (sports scores, stock tickers, weather, etc.)
- Site behavior (browsing history, cart information)
- Viewer Behavior (interactions, engagement, time spent with interactive elements)
- Viewer Information (first name, birth date)
- And more
Considerations for Implementing a Data‑Driven Video Strategy
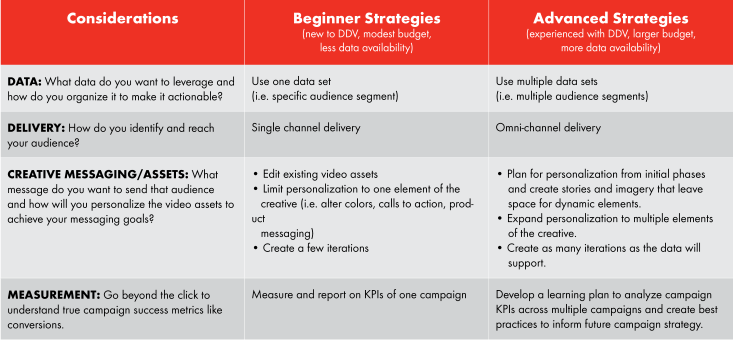
Capabilities Differ Based on Channel and Platform
Best Practices
- Data informs both audience and creative: Use data to identify different audiences and apply meaningful creative executions for each audience segment.
- Always consider where your ad will be seen:Think about how the video ad will fit into the multi‑screen ecosystem, take advantage of each screen’s strength, and consider the technology you can leverage to personalize your video.
- Think about the consumer journey: Messaging should change throughout the consumer journey. Feature the next best action for the viewer based on their engagement with the brand.
- Ensure data strategy is compliant with privacy regulation (i.e. GDPR, CCPA): First‑party data will be most impacted by privacy regulation so marketers should build a strategy that is not 100% reliant on first‑party data. One suggestion is to create a cascading logic for your data strategy. For example, first‑party data can be the priority data set but if the marketer can’t use it, they can then flow down to another type of data like contextual.
Challenges
- Data management: Keeping first‑party data organized and determining how to segment your own audiences can be challenging.
- Data quality: It is necessary to vet third‑party data sets to ensure that the vendor’s segmentation and modeling methods are sound and data is fresh. For more info, visit datalabel.org.
- Lack of resources: According to a Sailthru survey of UK and US marketers, more than 4 in 10 respondents said that a lack of time, people and money has inhibited their personalization efforts (Source: Sailthru, October 2017). Note: Vendors that offer managed services can alleviate resource challenges and help get personalization programs off the ground.
- Regulatory issues: As much as marketers are focused on reaching the right people, be mindful of also avoiding the wrong people (i.e. follow COPPA regulation, Legal Drinking Age (LDA) compliance)
Ad Delivery Considerations
VAST: VAST 4.x (i.e. VAST 4.0 and beyond) introduces the concept of “Ad Requests” and “VAST Interactive Templates” – both of which can be used to support some level of dynamic content.
VPAID (Note: The spec for interactive ads will transition from VPAID to SIMID): VPAID enables more complex levels of interaction for data‑driven video. For example, VPAID ad units can change in response to user interaction.
Measurement
- Go beyond the click: Traditional KPIs like video completion rate and clicks should be balanced against more accurate determinations of success, like conversions for performance‑based campaigns, and time‑spent, for branding and awareness campaigns.
- Establish benchmarks: Marketers can create benchmarks by conducting A/B testing. For example, run a generic version of the video first to establish benchmark for drop off and conversion rates. Then run the optimized video to understand how it performs against the benchmark.
- Test and iterate: Check campaign performance on a weekly or bi‑weekly basis and adjust your strategy based on performance. Testing can be as simple as an A/B test or as sophisticated as a multivariate test.
Data‑Driven Video Case Studies
The following interactive video case studies are examples from KERV Interactive. Click here for the full list of case studies.
1. Carhartt + KERV Interactive

- Campaign Goal: Drive traffic to Carhartt’s web site through interactive features in order to drive sales and raise awareness
- Data: Viewer behavior. Insights were gained regarding what specific Carhartt clothing items consumers were interacting with in the original Carhartt video asset. The viewer was served a sequential ad based on what Carhartt item they interacted with. The personalized video example provided was served to someone who interacted with the Carhartt jacket in the original video.
- Results: CTR: 2% CTR on personalized video versus 1% on original asset. Interaction Rate: 7% on personalized video versus 5% on original asset. Average time spent interacting with video: 45 sec with personalized video versus 30 seconds with original asset. Average time spent interacting with objects: 127 seconds.
- “Interaction Rate” Definition: Sum of all brand interactions within the video (against impressions). Interactions include scene saves, frame selects, object highlights (which have a qualified timer), object links, button clicks.
- “Average time spent interacting with video” definition: It is the difference between the first interactive time stamp and the last active time stamp within the player. Examples usually begin with either the Scene Save or Frame Select and the last time stamp is either a complete, a skip or a link out exit.
- “Average time spent interacting with objects” definition: The first time stamp fires when a user either clicks or taps on the object within the paused frame, when the user exits the text box or hovers off, there is an exit time stamp for this calculation. KERV Interactive then formulates the differences of these time stamps, by object, to determine average object level time spent or time spent interacting with a specific object.
2. Fisher & Paykel
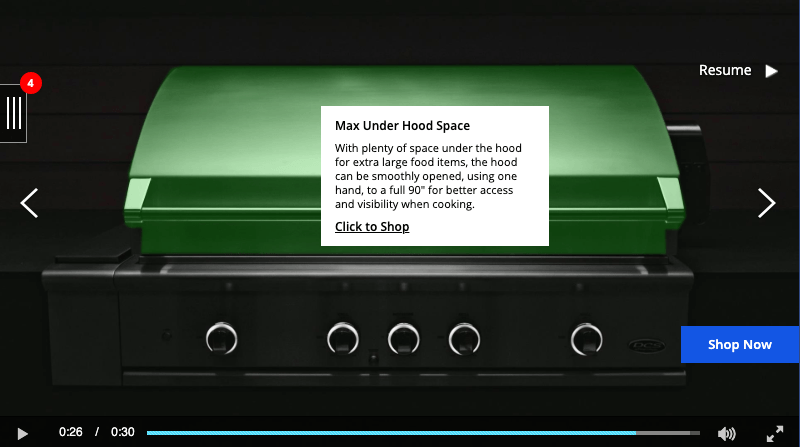
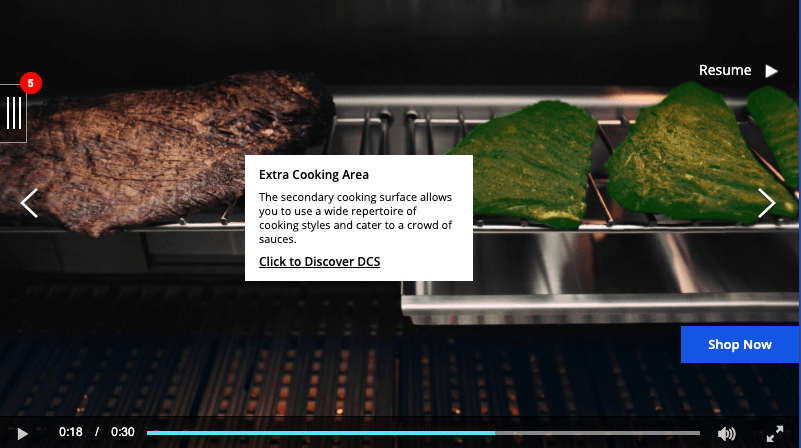
- Campaign Goal: Qualified clicks to site and time on‑site.
- Data: Viewer behavior, KERV Interactive targeted specific groups of interactors and excluded users who had already clicked out of the video asset.
- Results: 2.61% CTR on personalized video versus of 0.14% on original asset. 20% Interaction Rate versus 0.62% on original asset.
- “Interaction Rate” Definition: Sum of all brand interactions within the video (against impressions). Interactions include scene saves, frame selects, object highlights (which have a qualified timer), object links, button clicks.
